选择器✅
本主题涵盖CSS选择器的各种类型和使用方法,包括基础选择器、组合器、伪类、伪元素等。
CSS选择器有哪些类型?
答案
核心概念
CSS选择器是用于匹配HTML元素的模式,决定了样式规则应用到哪些元素上。CSS选择器模块提供了60多个选择器和5种组合器。
基础选择器类型
-
简单选择器(Simple Selectors)
- 通用选择器:
* - 类型选择器:
div、p、span - 类选择器:
.class-name - ID选择器:
#id-name - 属性选择器:
[attribute]、[attribute="value"]
- 通用选择器:
-
组合器(Combinators)
- 后代组合器:
" "(空格) - 子组合器:
> - 相邻兄弟组合器:
+ - 通用兄弟组合器:
~ - 列组合器:
||(较新)
- 后代组合器:
-
伪类选择器(Pseudo-classes)
- 状态伪类:
:hover、:focus、:active - 结构伪类:
:first-child、:nth-child() - 逻辑伪类:
:is()、:not()、:where()、:has()
- 状态伪类:
-
伪元素选择器(Pseudo-elements)
::before、::after::first-line、::first-letter::placeholder、::selection
代码示例
/* 简单选择器 */
* { margin: 0; } /* 通用选择器 */
div { display: block; } /* 类型选择器 */
.nav { background: blue; } /* 类选择器 */
#header { position: fixed; } /* ID选择器 */
[type="text"] { border: 1px solid; } /* 属性选择器 */
/* 组合器 */
nav ul { list-style: none; } /* 后代组合器 */
nav > ul { margin: 0; } /* 子组合器 */
h1 + p { margin-top: 0; } /* 相邻兄弟组合器 */
h1 ~ p { color: gray; } /* 通用兄弟组合器 */
/* 伪类 */
a:hover { color: red; } /* 状态伪类 */
li:first-child { font-weight: bold; } /* 结构伪类 */
:not(.active) { opacity: 0.5; } /* 逻辑伪类 */
/* 伪元素 */
p::before { content: "→ "; } /* 生成内容 */
input::placeholder { color: gray; } /* 占位符样式 */
/* 复杂选择器组合 */
.nav ul li:first-child a:hover {
background: lightblue;
}
选择器分类表
| 分类 | 选择器 | 语法示例 | 用途 |
|---|---|---|---|
| 基础 | 通用选择器 | * | 选择所有元素 |
| 基础 | 类型选择器 | div | 选择特定类型元素 |
| 基础 | 类选择器 | .class | 选择特定类的元素 |
| 基础 | ID选择器 | #id | 选择特定ID的元素 |
| 基础 | 属性选择器 | [attr] | 选择具有特定属性的元素 |
| 组合 | 后代选择器 | A B | 选择A内部的B元素 |
| 组合 | 子选择器 | A > B | 选择A的直接子元素B |
| 组合 | 相邻兄弟 | A + B | 选择紧接在A后的B |
| 组合 | 通用兄弟 | A ~ B | 选择A后面的所有B |
CSS选择器优先级如何计算?
答案
核心概念
CSS选择器优先级(Specificity)决定了当多个规则应用到同一元素时,哪个规则会生效。优先级通过四位数字系统计算。
优先级计算规则
优先级由四部分组成:(a, b, c, d)
-
a位:内联样式
- 内联样式:1
- 其他:0
-
b位:ID选择器
- 每个ID选择器:+1
-
c位:类、属性、伪类选择器
- 每个类选择器:+1
- 每个属性选择器:+1
- 每个伪类选择器:+1
-
d位:元素、伪元素选择器
- 每个元素选择器:+1
- 每个伪元素选择器:+1
特殊规则
!important:最高优先级- 通用选择器
*:不增加优先级 - 组合器(
+,>,~,
代码示例
/* 优先级计算示例 */
/* (0,0,0,1) = 1 */
p { color: black; }
/* (0,0,1,0) = 10 */
.text { color: red; }
/* (0,1,0,0) = 100 */
#title { color: blue; }
/* (0,0,1,1) = 11 */
p.text { color: green; }
/* (0,1,1,1) = 111 */
#title.text p { color: purple; }
/* (0,0,2,1) = 21 */
.nav .item a { color: orange; }
/* (0,0,0,3) = 3 */
nav ul li { color: gray; }
/* 最高优先级 */
p { color: yellow !important; }
/* 实际应用场景 */
.button {
background: blue; /* (0,0,1,0) = 10 */
}
.button.primary {
background: red; /* (0,0,2,0) = 20,优先级更高 */
}
#submit.button {
background: green; /* (0,1,1,0) = 110,优先级最高 */
}
优先级比较表
| 选择器 | 优先级值 | 说明 |
|---|---|---|
* | (0,0,0,0) | 通用选择器无优先级 |
li | (0,0,0,1) | 元素选择器 |
li:first-line | (0,0,0,2) | 元素+伪元素 |
ul li | (0,0,0,2) | 两个元素选择器 |
ul ol+li | (0,0,0,3) | 三个元素选择器 |
h1 + *[rel=up] | (0,0,1,1) | 一个属性+一个元素 |
ul ol li.red | (0,0,1,3) | 一个类+三个元素 |
li.red.level | (0,0,2,1) | 两个类+一个元素 |
#x34y | (0,1,0,0) | 一个ID |
style="" | (1,0,0,0) | 内联样式 |
避免优先级冲突的最佳实践
- 避免使用
!important - 尽量使用类选择器而非ID选择器
- 保持选择器简洁,避免过度嵌套
- 使用CSS方法论(如BEM)管理样式
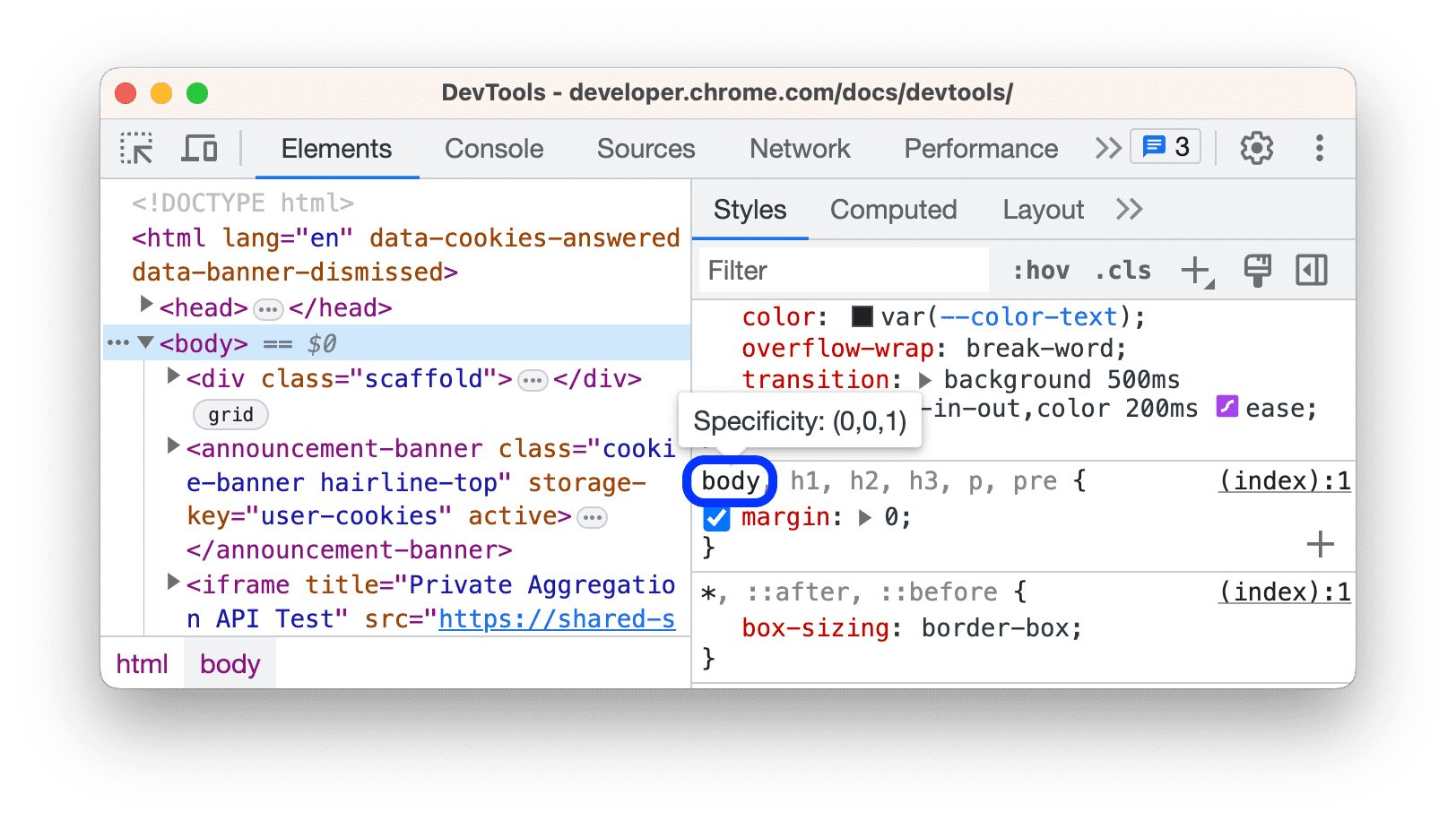
可以直接使用 chrome 查看优先级。详见 View selector specificity
鼠标悬浮在选择器上就会显示如下的优先级说明, (0,0,1) 数字越靠左优先级越高,从左到右依次表示 id,类/属性,元素
常用的CSS伪类选择器有哪些?
答案
核心概念
伪类选择器用于选择处于特定状态的元素,这些状态信息不包含在文档树中,而是基于用户交互、表单状态、元素位置等动态条件。
状态伪类
/* 链接状态 */
a:link { color: blue; } /* 未访问的链接 */
a:visited { color: purple; } /* 已访问的链接 */
a:hover { color: red; } /* 鼠标悬停 */
a:active { color: orange; } /* 正在点击 */
a:focus { outline: 2px solid; } /* 获得焦点 */
/* 表单状态 */
input:enabled { background: white; } /* 可用状态 */
input:disabled { background: gray; } /* 禁用状态 */
input:checked { transform: scale(1.1); } /* 选中状态 */
input:required { border-color: red; } /* 必填字段 */
input:optional { border-color: gray; } /* 可选字段 */
input:valid { border-color: green; } /* 验证通过 */
input:invalid { border-color: red; } /* 验证失败 */
结构伪类
/* 子元素位置 */
p:first-child { margin-top: 0; } /* 第一个子元素 */
p:last-child { margin-bottom: 0; } /* 最后一个子元素 */
p:only-child { text-align: center; } /* 唯一子元素 */
/* 类型位置 */
h2:first-of-type { color: blue; } /* 同类型第一个 */
h2:last-of-type { color: red; } /* 同类型最后一个 */
h2:only-of-type { font-size: 2em; } /* 同类型唯一 */
/* 数字选择 */
li:nth-child(2n) { background: #f0f0f0; } /* 偶数项 */
li:nth-child(2n+1) { background: white; } /* 奇数项 */
li:nth-child(3n) { color: red; } /* 每3个 */
li:nth-child(-n+3) { font-weight: bold; } /* 前3个 */
/* 实际应用 */
.grid-item:nth-child(3n+1) {
clear: left; /* 每行第一个元素清除浮动 */
}
tr:nth-child(even) {
background: #f9f9f9; /* 表格斑马纹效果 */
}
现代逻辑伪类
/* :is() - 匹配列表中任意选择器 */
:is(h1, h2, h3) { margin: 1em 0; }
/* 等同于 */
h1, h2, h3 { margin: 1em 0; }
/* :not() - 否定选择器 */
button:not(.disabled) { cursor: pointer; }
input:not([type="hidden"]) { display: block; }
/* :where() - 零优先级的 :is() */
:where(h1, h2, h3) { margin: 1em 0; }
/* :has() - 父选择器(较新特性) */
.card:has(img) { padding: 0; } /* 包含图片的卡片 */
form:has(input:invalid) { border: 2px solid red; } /* 包含无效输入的表单 */
目标和根伪类
/* :target - 锚点目标 */
#section1:target { background: yellow; }
/* :root - 文档根元素 */
:root {
--primary-color: #007bff;
--font-size: 16px;
}
/* :empty - 空元素 */
p:empty { display: none; }
/* :defined - 自定义元素 */
my-component:defined { opacity: 1; }
常用伪类总结表
| 分类 | 伪类 | 用途 | 示例 |
|---|---|---|---|
| 状态 | :hover | 鼠标悬停 | a:hover { color: red; } |
| 状态 | :focus | 获得焦点 | input:focus { border-color: blue; } |
| 状态 | :active | 正在激活 | button:active { transform: scale(0.95); } |
| 表单 | :checked | 选中状态 | input:checked + label { color: green; } |
| 表单 | :disabled | 禁用状态 | input:disabled { opacity: 0.5; } |
| 结构 | :first-child | 第一个子元素 | li:first-child { list-style: none; } |
| 结构 | :nth-child() | 第n个子元素 | tr:nth-child(odd) { background: #f9f9f9; } |
| 逻辑 | :not() | 否定选择 | button:not(.primary) { background: gray; } |
| 逻辑 | :is() | 匹配任意 | :is(h1,h2,h3) { margin: 0; } |
CSS属性选择器如何使用?
答案
核心概念
属性选择器根据元素的属性及其值来选择元素,提供了灵活的选择机制,特别适用于表单元素和自定义属性。
基础属性选择器
/* [attribute] - 存在属性 */
input[required] { border: 2px solid red; }
img[alt] { border: 1px solid green; }
/* [attribute="value"] - 精确匹配 */
input[type="text"] { padding: 8px; }
a[href="#"] { color: gray; }
button[disabled="disabled"] { opacity: 0.5; }
值匹配属性选择器
/* [attribute~="value"] - 词匹配(空格分隔) */
.box[class~="active"] { background: blue; }
/* 匹配 class="box active large" */
/* [attribute|="value"] - 前缀匹配(连字符分隔) */
[lang|="en"] { font-family: "English Font"; }
/* 匹配 lang="en-US", lang="en-GB" */
/* [attribute^="value"] - 开头匹配 */
a[href^="https://"] { color: green; } /* HTTPS链接 */
a[href^="mailto:"] { color: orange; } /* 邮件链接 */
a[href^="tel:"] { color: blue; } /* 电话链接 */
/* [attribute$="value"] - 结尾匹配 */
a[href$=".pdf"] { background: url(pdf-icon.png); }
img[src$=".jpg"], img[src$=".png"] { border: 1px solid; }
/* [attribute*="value"] - 包含匹配 */
input[name*="email"] { background: lightblue; }
a[href*="github"] { color: black; }
大小写敏感性
/* 默认大小写敏感 */
[data-status="Active"] { color: green; }
/* i 标志:大小写不敏感 */
[data-status="active" i] { color: green; }
/* 匹配 "Active", "ACTIVE", "active" */
/* s 标志:强制大小写敏感(默认行为) */
[data-status="active" s] { color: green; }
实际应用场景
/* 表单样式 */
/* 必填字段 */
input[required] {
border-left: 3px solid #e74c3c;
}
/* 不同输入类型 */
input[type="email"] { background: url(email-icon.png) no-repeat right; }
input[type="password"] { background: url(lock-icon.png) no-repeat right; }
input[type="search"] { border-radius: 20px; }
/* 表单验证状态 */
input[aria-invalid="true"] { border-color: red; }
input[aria-invalid="false"] { border-color: green; }
/* 链接类型 */
/* 外部链接 */
a[href^="http"]:not([href*="yourdomain.com"]) {
background: url(external-link.png) no-repeat right;
padding-right: 20px;
}
/* 下载链接 */
a[href$=".zip"], a[href$=".rar"], a[href$=".7z"] {
background: url(archive-icon.png) no-repeat left;
padding-left: 20px;
}
/* 自定义数据属性 */
[data-tooltip] {
position: relative;
cursor: help;
}
[data-tooltip]:hover::after {
content: attr(data-tooltip);
position: absolute;
background: black;
color: white;
padding: 5px;
border-radius: 3px;
top: 100%;
left: 50%;
transform: translateX(-50%);
}
/* 状态管理 */
[data-state="loading"] { opacity: 0.5; }
[data-state="error"] { border-color: red; }
[data-state="success"] { border-color: green; }
/* 响应式图片 */
img[data-sizes="small"] { max-width: 200px; }
img[data-sizes="medium"] { max-width: 400px; }
img[data-sizes="large"] { max-width: 800px; }
属性选择器组合使用
/* 多个属性组合 */
input[type="text"][required] {
border: 2px solid orange;
}
/* 与其他选择器组合 */
.form-group input[type="text"]:focus {
box-shadow: 0 0 5px blue;
}
/* 复杂匹配 */
a[href^="https://"][href*="github"][href$=".com"] {
background: url(github-icon.png) no-repeat left;
}
属性选择器总结表
| 选择器 | 含义 | 示例 | 匹配 |
|---|---|---|---|
[attr] | 存在属性 | [title] | 任何有title属性的元素 |
[attr="val"] | 精确匹配 | [type="button"] | type属性值为"button" |
[attr~="val"] | 词匹配 | [class~="nav"] | class包含"nav"词 |
[attr|="val"] | 前缀匹配 | [lang|="en"] | lang以"en-"开头或等于"en" |
[attr^="val"] | 开头匹配 | [href^="https"] | href以"https"开头 |
[attr$="val"] | 结尾匹配 | [src$=".jpg"] | src以".jpg"结尾 |
[attr*="val"] | 包含匹配 | [href*="github"] | href包含"github" |
现代CSS选择器有哪些新特性?
答案
核心概念
现代CSS引入了多个新的选择器特性,提供更强大的选择能力和更好的性能,包括:has()、:is()、:where()等逻辑选择器。
:has() 父选择器
:has()是CSS中的"父选择器",可以根据子元素的存在选择父元素。
/* 基础用法 */
.card:has(img) { padding: 0; } /* 包含图片的卡片 */
.card:has(> img) { padding: 0; } /* 直接子元素为图片的卡片 */
/* 表单验证 */
form:has(input:invalid) {
border: 2px solid red;
}
.form-group:has(input:focus) {
background: #f0f8ff;
}
/* 复杂组合 */
article:has(h2):has(p) { /* 同时包含h2和p的article */
margin-bottom: 2rem;
}
.sidebar:has(.widget:nth-child(n+3)) { /* 包含3个或更多widget的sidebar */
display: grid;
grid-template-columns: 1fr 1fr;
}
/* 实际应用场景 */
/* 根据内容调整布局 */
.product:has(.discount) { border-color: red; }
.product:has(.out-of-stock) { opacity: 0.5; }
/* 导航状态 */
nav:has(a.active) { background: #f5f5f5; }
:is() 和 :where() 逻辑选择器
/* :is() - 匹配列表中的任意选择器 */
:is(h1, h2, h3, h4, h5, h6) {
margin: 0 0 1rem 0;
font-weight: bold;
}
/* 等同于传统写法,但更简洁 */
h1, h2, h3, h4, h5, h6 {
margin: 0 0 1rem 0;
font-weight: bold;
}
/* 复杂嵌套简化 */
:is(.sidebar, .content) :is(h1, h2) {
color: #333;
}
/* :where() - 零优先级的 :is() */
:where(h1, h2, h3) { margin: 1rem 0; } /* 优先级为0 */
:is(h1, h2, h3) { margin: 1rem 0; } /* 优先级为最高的选择器 */
/* 实际应用 */
/* 按钮样式 */
:is(.btn, .button, [role="button"]) {
padding: 8px 16px;
border: none;
border-radius: 4px;
cursor: pointer;
}
/* 链接状态 */
:is(a, button):is(:hover, :focus) {
outline: 2px solid blue;
}
:not() 增强版
/* 传统 :not() - 只能接受简单选择器 */
input:not([type="hidden"]) { display: block; }
/* 现代 :not() - 可以接受复杂选择器 */
p:not(.intro, .summary) { color: gray; }
section:not(:has(h1, h2, h3)) { /* 不包含标题的section */
padding-top: 0;
}
/* 排除多个条件 */
button:not(.disabled):not([disabled]):not(.loading) {
cursor: pointer;
}
/* 与其他选择器组合 */
.list-item:not(:first-child):not(:last-child) {
border-top: 1px solid #eee;
border-bottom: 1px solid #eee;
}
容器查询选择器(@container)
/* 容器查询 - 基于容器尺寸的样式 */
.card-container {
container-type: inline-size;
container-name: card;
}
@container card (min-width: 300px) {
.card {
display: flex;
gap: 1rem;
}
.card-image {
flex: 0 0 100px;
}
}
@container (min-width: 500px) {
.card {
grid-template-columns: 1fr 2fr;
}
}
其他现代选择器特性
/* :target-within - 包含目标元素的祖先 */
.section:target-within { background: #f0f8ff; }
/* :focus-within - 包含焦点元素的祖先 */
.form-group:focus-within { box-shadow: 0 0 5px blue; }
/* :focus-visible - 键盘导航焦点 */
button:focus-visible { outline: 2px solid orange; }
/* :user-invalid - 用户交互后的验证状态 */
input:user-invalid { border-color: red; }
/* :popover-open - 打开的弹出框 */
[popover]:popover-open {
background: white;
border: 1px solid #ccc;
}
/* 自定义元素选择器 */
:defined { opacity: 1; } /* 已定义的自定义元素 */
:custom-state(loading) { opacity: 0.5; } /* 自定义状态 */
实际项目应用示例
/* 响应式设计增强 */
.layout:has(.sidebar) {
display: grid;
grid-template-columns: 250px 1fr;
}
.layout:not(:has(.sidebar)) {
max-width: 800px;
margin: 0 auto;
}
/* 表单增强 */
.form-field:has(input:invalid) .label {
color: red;
}
.form-field:has(input:valid) .icon {
color: green;
}
/* 动态内容布局 */
.post:has(.featured-image) {
display: grid;
grid-template-columns: 200px 1fr;
gap: 1rem;
}
.post:not(:has(.featured-image)) .content {
max-width: 65ch;
}
/* 状态管理 */
.component:is(.loading, .error) .content {
opacity: 0.5;
}
.component:where(.success, .completed) {
border-color: green;
}
浏览器支持和回退策略
/* 特性检测 */
@supports selector(:has(*)) {
.card:has(img) { padding: 0; }
}
@supports not selector(:has(*)) {
.card.has-image { padding: 0; } /* 回退样式 */
}
/* 渐进增强 */
.form-group { background: white; } /* 基础样式 */
.form-group:has(input:focus) { /* 增强样式 */
background: #f0f8ff;
}
现代选择器优势总结
- 更强表达力:能表达更复杂的选择逻辑
- 更好性能:原生实现比JavaScript操作DOM更高效
- 代码简化:减少冗余代码和JavaScript依赖
- 响应式增强:基于内容和状态的响应式设计
- 可维护性:逻辑集中在CSS中,易于维护
如何评估 css 选择器性能?
答案
参考规范 Match a Selector Against an Element css 采用从右往左的匹配。选择器寻找文档树中的元素,本质是一个树匹配,所以在书写选择器的时候核心记住
- 尽量减少选择器的深度
- 尽可能通过 ID 或类选择器来匹配元素,减少通用属性或者标签选择器的使用,使右匹配更高效
为什么会是右匹配,从复杂度分析角度
- 时间复杂度,右匹配低于左匹配。左匹配需要递归遍历子树,右匹配只需要遍历树后,进行回溯匹配。复杂度更低
- 空间复杂度,右匹配只需要保存当前匹配状态,而左匹配在未匹配上时,需要保存整个候选链条浪费更多空间
延伸阅读
- Analyze CSS selector performance during Recalculate Style events 详解讲解如何利用性能面板中的 Selector Stats 功能来分析 CSS 选择器的性能。
- The truth about CSS selector performance css 性能真相, 由于 IE 也使用了 chromium 内核,所以也可以采用 Selector Stats 来分析选择器性能
- Analyze CSS selector performance during Recalculate Style events Edge CSS 选择器性能分析说明
- 选择器性能
- CSS Selector Performance has changed! 比较详细的讲解了 css 的匹配优化策略'
- 样式失效的计算